Programming
Split Command Sample Code (VB NET)
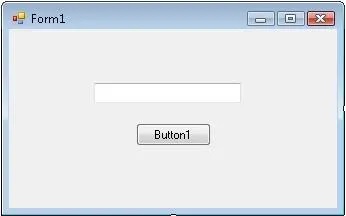
0Preparations : 1 Textbox and 1 Button
Code :
Private Sub Button1_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim strInput As Array 'make array variable
Dim strResult1 As String 'text variable
Dim strResult2 As String 'another text variable
Try
strInput = Split(TextBox1.Text, " ")
'split the textbox if there is space.
'you can also use chr(32) to replace " "
strResult1 = strInput(0) 'split first text
strResult2 = strInput(1) 'split second text
MsgBox(strResult1 + strResult2)
'combine first and second text with no space
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
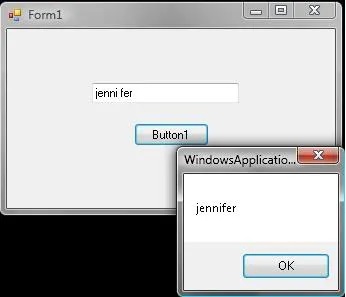
End SubTest the code, type space character between 2 words :
What we have done here?
Explanation :
- We have 2 words with a space character (“jenni” and “fer”)
- We split those words using “Split” command into array, the process is identified with space character, so we had 2 lines.
- We combine those words back together in one line, but this time with no space character in it.
Getting IP Address (VB NET 2008)
0Note: if you’re not a beginner and just want to look for the code, you may skip these 1-6 steps and go straight to the sample code.
1) Let’s start with new project “Windows forms application”
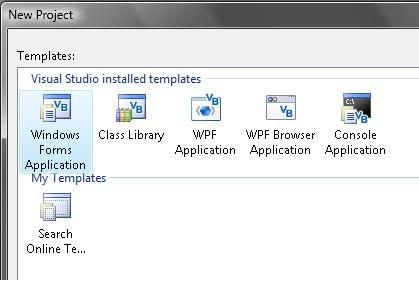
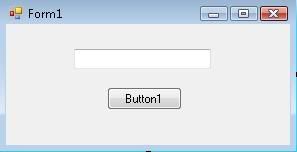
2) Put one TextBox and a Button in the Form
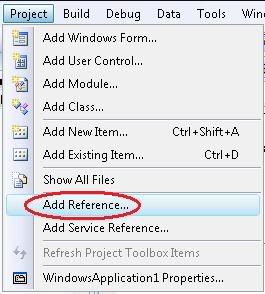
3) Add reference to our project by clicking : Project –> Add Reference
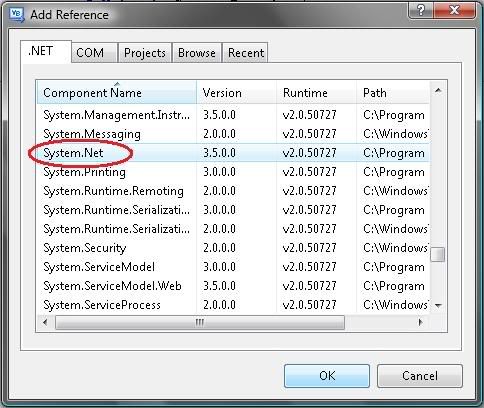
4) Scroll down and select “System.Net” as our reference. Click OK to proceed.
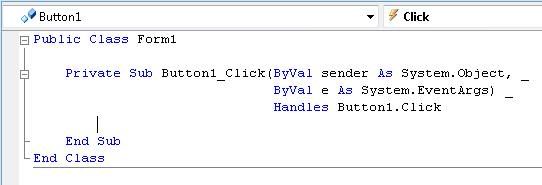
5) Open the Coding Window or you can just simply double click on the Button1, or you can also use F7 for shortcut.
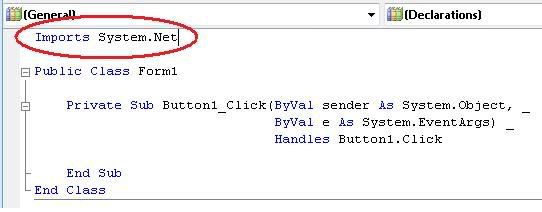
6) Type “Imports System.Net” in General as shown in the picture below
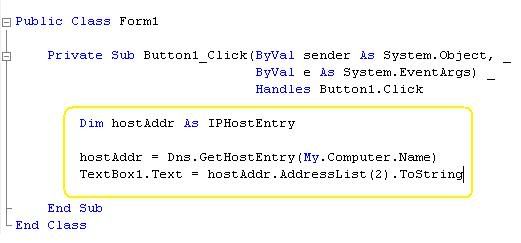
7) Now the code part, on your Button1_Click event add this code as shown in the picture below
8) Run your program or press F5
Access Database Connection (OLEDB) – VB NET 2008
0Here, I will show you how to make a connection to MS Access 2007 database with VB NET 2008 using wizard. If you’re looking for the sample using code, then this is not what you’re looking for.
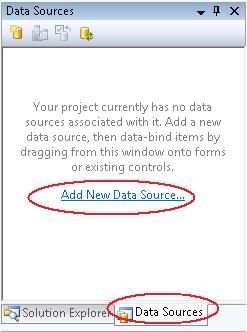
1) Start with NEW windows form projec. When new project has been created, click the “Data Source” tab and choose “Add New Data Source”
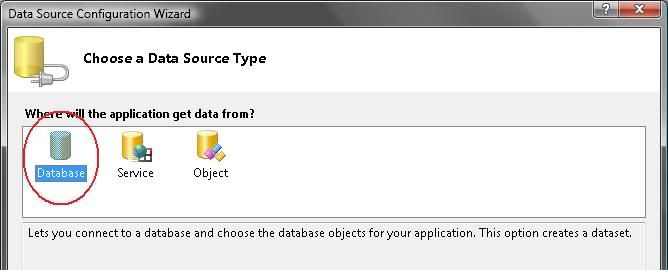
2) Choose “Database” and then click OK
3) Click “New Connection”
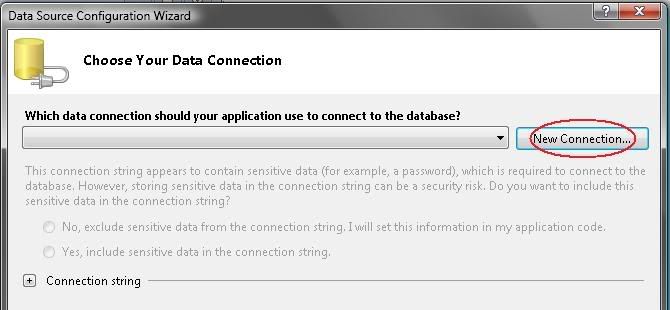
4) on Default, the connection is set to SQL, to make database connection using Access then you need to change it as in the picture below.
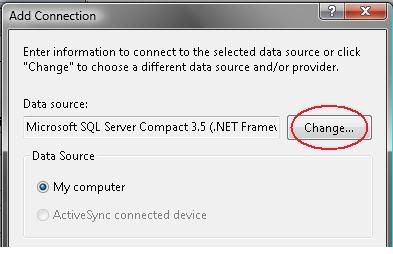
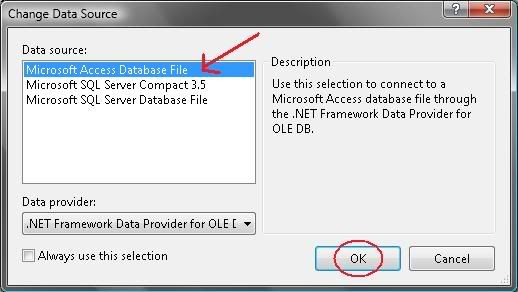
5) Select “Microsoft Access Database File” then click OK.
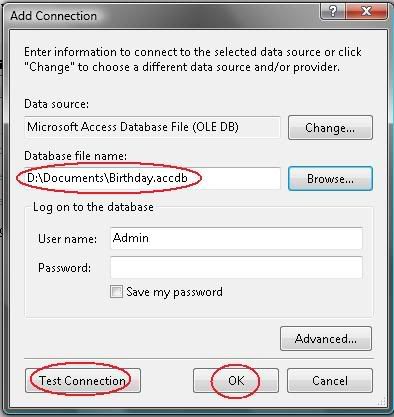
6) The Data Source has been changed to “Microsoft Access Database File (OLEDB)”. Now you need to load your database file to the project. To do this, click “Browse” and point to your database file then click OK to proceed. After all set up, you can click on “Test Connection” to check the connection status. Once you ready, continue to next step by clicking OK button. (see picture below)
7) You might see this pop up message, just click YES to copy your database file into project folder. From here, just click on “NEXT” button until you reach the part as seen in the picture in STEP 8
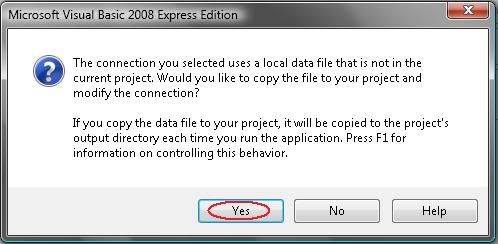
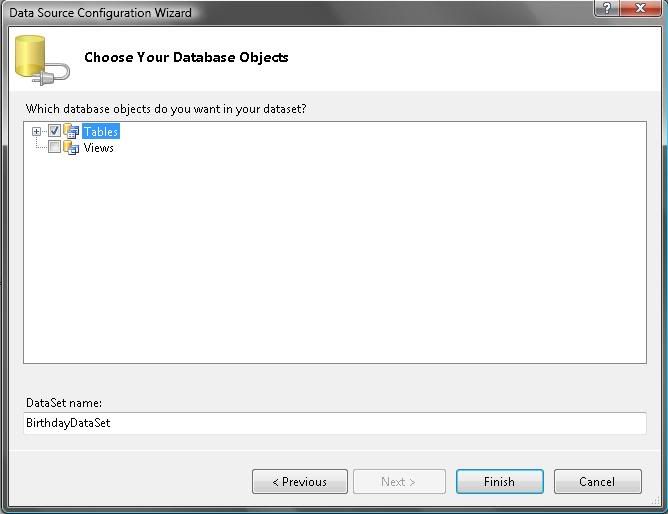
8) Make sure the “Tables” is checked and click “Finish” to proceed to the next step.
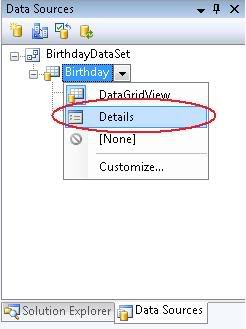
9) Now back to Data Sources window, left click Birthday Table and choose “Details” (see picture below)
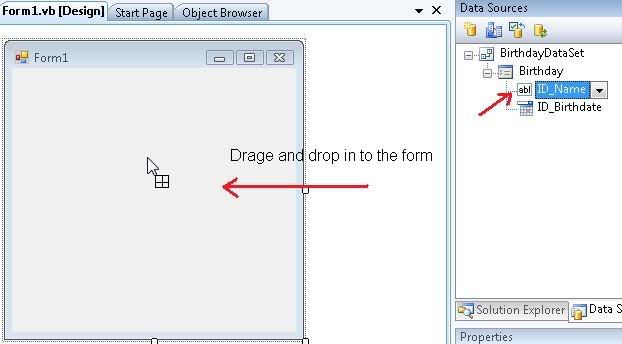
10) Final step in this tutorial. While holding mouse left click on the icon beside “ID_Name”, drag and drop it to the form. Do the same way for “ID_Birthdate”.
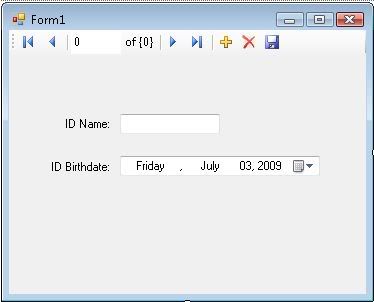
Finally, your form might look like this picture below. To navigate through the records in your database, use navigation button on top of the form. You can also execute : Add and Remove command. Press F5 to run the program. (Tips: to see larger picture size, right click on pictures and choose “view image”)
GetAsyncKeyState API Definition
0I was wondering about a way to get the keyboard strokes & read them. This windows api can be used from all sorts of keylogger hacking tricks to useful shortcut keys in an OS that you would like to define. here is a small code snippet with explanation:
This snippet shows the user how to get the key pressed. That is if the user presses control key that key is identified. Using this we can develop applications with greater flexibility. For example we can make an application to close if a key is pressed and so on.
This code is basically a smaller one with greater potential. It just contains three lines of code.
Public Declare Function GetAsyncKeyState Lib "user32" (ByVal vKey As Long) As IntegerOn Error Resume Next
'To check wheteher Control key is pressed
If GetAsyncKeyState(17) Then
msgbox "Control key pressed"
End IfVB.NET: How to sort listview by clicked column
3One of my favorite .NET control is the ListView. It is very useful for displaying multiple records on a spreadsheet format. Column sorting is one the feature of spreadsheet applications that most of end-users are used to. Unfortunately, this is not readily available as property in VB.NET. The ListView Sorting property only sorts items and not the sub-items so it can’t be use if we want to allow the user to sort your list by any clicked column.
To make your ListView application capable of column sorting, follow these steps:
1. On your existing project, add a new class with following code:
Imports System.Collections
Public Class clsListviewSorter
Implements System.Collections.IComparer ' Implements a comparer Implements IComparer
Private m_ColumnNumber As Integer
Private m_SortOrder As SortOrder
Public Sub New(ByVal column_number As Integer, ByVal sort_order As SortOrder)
m_ColumnNumber = column_number
m_SortOrder = sort_order
End Sub
' Compare the items in the appropriate column
Public Function Compare(ByVal x As Object, ByVal y As Object) As Integer Implements IComparer.Compare
Dim item_x As ListViewItem = DirectCast(x, ListViewItem)
Dim item_y As ListViewItem = DirectCast(y, ListViewItem)
' Get the sub-item values.
Dim string_x As String
If item_x.SubItems.Count <= m_ColumnNumber Then
string_x = ""
Else
string_x = item_x.SubItems(m_ColumnNumber).Text
End If
Dim string_y As String
If item_y.SubItems.Count <= m_ColumnNumber Then
string_y = ""
Else
string_y = item_y.SubItems(m_ColumnNumber).Text
End If
' Compare them.
If m_SortOrder = SortOrder.Ascending Then
If IsNumeric(string_x) And IsNumeric(string_y) Then
Return (Val(string_x).CompareTo(Val(string_y)))
ElseIf IsDate(string_x) And IsDate(string_y) Then
Return (DateTime.Parse(string_x).CompareTo(DateTime.Parse(string_y)))
Else
Return (String.Compare(string_x, string_y))
End If
Else
If IsNumeric(string_x) And IsNumeric(string_y) Then
Return (Val(string_y).CompareTo(Val(string_x)))
ElseIf IsDate(string_x) And IsDate(string_y) Then
Return (DateTime.Parse(string_y).CompareTo(DateTime.Parse(string_x)))
Else
Return (String.Compare(string_y, string_x))
End If
End If
End Function
End Class2. Declare a private variable on the form where the listview you want to be sorted is located.
Private m_SortingColumn As ColumnHeader
3. Then on the listview’s ColumnClick event, add the following code
Private Sub ListView1_ColumnClick(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.Windows.Forms.ColumnClickEventArgs) Handles ListView1.ColumnClick
' Get the new sorting column.
Dim new_sorting_column As ColumnHeader = ListView1.Columns(e.Column)
' Figure out the new sorting order.
Dim sort_order As System.Windows.Forms.SortOrder
If m_SortingColumn Is Nothing Then
' New column. Sort ascending.
sort_order = SortOrder.Ascending
Else ' See if this is the same column.
If new_sorting_column.Equals(m_SortingColumn) Then
' Same column. Switch the sort order.
If m_SortingColumn.Text.StartsWith("> ") Then
sort_order = SortOrder.Descending
Else
sort_order = SortOrder.Ascending
End If
Else
' New column. Sort ascending.
sort_order = SortOrder.Ascending
End If
' Remove the old sort indicator.
m_SortingColumn.Text = m_SortingColumn.Text.Substring(2)
End If
' Display the new sort order.
m_SortingColumn = new_sorting_column
If sort_order = SortOrder.Ascending Then
m_SortingColumn.Text = "> " & m_SortingColumn.Text
Else
m_SortingColumn.Text = "< " & m_SortingColumn.Text
End If
' Create a comparer.
ListView1.ListViewItemSorter = New clsListviewSorter(e.Column, sort_order)
' Sort.
ListView1.Sort()
End Sub
There you have it, test your listview application and it should be sorting by the column clicked.
How to Change the ‘sa’ password in SQL Server 2005,2008
0Method 1:
Login into SQL Server using Windows Authentication.
In Object Explorer, open Security folder, open Logins folder. Right Click on SA account and go to Properties.
Change SA password, and confirm it. Click OK.
Make sure to restart the SQL Server and all its services and test new password by log into system using SA login and new password.
Method 2:
1.Open the SQL Server express management studio
2.Connect to SQL Server using windows authentication

3.Right click the server name and choose properties

4.Go to security tab. Change server authentication to “SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode”

5.Click OK and restart SQL Server
6.Go to SQL Server studio management express
7.Expand the server and choose security and expand logins

8.Right click on SA, from properties modify the password and confirm password
Method 3: (From Command prompt)
1. Start a command prompt by typing Start – Run – cmd
2. Enter the following commands, pressing Enter after each line
OSQL -S yourservername -E
1> EXEC sp_password NULL, ‘yourpassword’, ’sa’
2> GO
Where yourservername is the name of your server and yourpassword is the new sa account password. Type exit twice to return to the server desktop.
Method 4: (Query) my personal favorite
Make a new query & write in it, then run.
USE [master]
GO
ALTER LOGIN [sa] WITH DEFAULT_DATABASE=[master],
DEFAULT_LANGUAGE=[us_english], CHECK_EXPIRATION=ON, CHECK_POLICY=ON
GO
USE [master]
GO
ALTER LOGIN [sa] WITH PASSWORD=N’<insert_new_password_here>’ MUST_CHANGE
GODateTime.ToString() Patterns
0All the patterns:
0 MM/dd/yyyy 08/22/2006
1 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy Tuesday, 22 August 2006
2 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30
3 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy hh:mm tt Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30 AM
4 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy H:mm Tuesday, 22 August 2006 6:30
5 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy h:mm tt Tuesday, 22 August 2006 6:30 AM
6 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30:07
7 MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm 08/22/2006 06:30
8 MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm tt 08/22/2006 06:30 AM
9 MM/dd/yyyy H:mm 08/22/2006 6:30
10 MM/dd/yyyy h:mm tt 08/22/2006 6:30 AM
10 MM/dd/yyyy h:mm tt 08/22/2006 6:30 AM
10 MM/dd/yyyy h:mm tt 08/22/2006 6:30 AM
11 MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss 08/22/2006 06:30:07
12 MMMM dd August 22
13 MMMM dd August 22
14 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd’T’HH’:’mm’:’ss.fffffffK 2006-08-22T06:30:07.7199222-04:00
15 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd’T’HH’:’mm’:’ss.fffffffK 2006-08-22T06:30:07.7199222-04:00
16 ddd, dd MMM yyyy HH’:’mm’:’ss ‘GMT’ Tue, 22 Aug 2006 06:30:07 GMT
17 ddd, dd MMM yyyy HH’:’mm’:’ss ‘GMT’ Tue, 22 Aug 2006 06:30:07 GMT
18 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd’T’HH’:’mm’:’ss 2006-08-22T06:30:07
19 HH:mm 06:30
20 hh:mm tt 06:30 AM
21 H:mm 6:30
22 h:mm tt 6:30 AM
23 HH:mm:ss 06:30:07
24 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd HH’:’mm’:’ss’Z’ 2006-08-22 06:30:07Z
25 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30:07
26 yyyy MMMM 2006 August
27 yyyy MMMM 2006 August
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘d’ ) :
0 MM/dd/yyyy 08/22/2006
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘D’ ) :
0 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy Tuesday, 22 August 2006
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘f’ ) :
0 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30
1 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy hh:mm tt Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30 AM
2 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy H:mm Tuesday, 22 August 2006 6:30
3 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy h:mm tt Tuesday, 22 August 2006 6:30 AM
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘F’ ) :
0 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30:07
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘g’ ) :
0 MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm 08/22/2006 06:30
1 MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm tt 08/22/2006 06:30 AM
2 MM/dd/yyyy H:mm 08/22/2006 6:30
3 MM/dd/yyyy h:mm tt 08/22/2006 6:30 AM
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘G’ ) :
0 MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss 08/22/2006 06:30:07
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘m’ ) :
0 MMMM dd August 22
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘r’ ) :
0 ddd, dd MMM yyyy HH’:’mm’:’ss ‘GMT’ Tue, 22 Aug 2006 06:30:07 GMT
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘s’ ) :
0 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd’T’HH’:’mm’:’ss 2006-08-22T06:30:07
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘u’ ) :
0 yyyy’-‘MM’-‘dd HH’:’mm’:’ss’Z’ 2006-08-22 06:30:07Z
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘U’ ) :
0 dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Tuesday, 22 August 2006 06:30:07
The patterns for DateTime.ToString ( ‘y’ ) :
0 yyyy MMMM 2006 August
/ Represents the date separator defined in the current DateTimeFormatInfo..::.DateSeparator property. This separator is used to differentiate years, months, and days.
” Represents a quoted string (quotation mark). Displays the literal value of any string between two quotation marks (“). Your application should precede each quotation mark with an escape character (\).
‘ Represents a quoted string (apostrophe). Displays the literal value of any string between two apostrophe (‘) characters.
%c Represents the result associated with a c custom format specifier, when the custom date and time format string consists solely of that custom format specifier. That is, to use the d, f, F, h, m, s, t, y, z, H, or M custom format specifier by itself, the application should specify %d, %f, %F, %h, %m, %s, %t, %y, %z, %H, or %M. For more information about using a single format specifier, see Using Single Custom Format Specifiers.
Building a custom DateTime.ToString Patterns
The following details the meaning of each pattern character. Not the K and z character.
d Represents the day of the month as a number from 1 through 31. A single-digit day is formatted without a leading zero
dd Represents the day of the month as a number from 01 through 31. A single-digit day is formatted with a leading zero
ddd Represents the abbreviated name of the day of the week (Mon, Tues, Wed etc)
dddd Represents the full name of the day of the week (Monday, Tuesday etc)
h 12-hour clock hour (e.g. 7)
hh 12-hour clock, with a leading 0 (e.g. 07)
H 24-hour clock hour (e.g. 19)
HH 24-hour clock hour, with a leading 0 (e.g. 19)
m Minutes
mm Minutes with a leading zero
M Month number
MM Month number with leading zero
MMM Abbreviated Month Name (e.g. Dec)
MMMM Full month name (e.g. December)
s Seconds
ss Seconds with leading zero
t Abbreviated AM / PM (e.g. A or P)
tt AM / PM (e.g. AM or PM
y Year, no leading zero (e.g. 2001 would be 1)
yy Year, leadin zero (e.g. 2001 would be 01)
yyy Year, (e.g. 2001 would be 2001)
yyyy Year, (e.g. 2001 would be 2001)
K Represents the time zone information of a date and time value (e.g. +05:00)
z With DateTime values, represents the signed offset of the local operating system’s time zone from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), measured in hours. (e.g. +6)
zz As z but with leadin zero (e.g. +06)
zzz With DateTime values, represents the signed offset of the local operating system’s time zone from UTC, measured in hours and minutes. (e.g. +06:00)
f Represents the most significant digit of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the tenths of a second in a date and time value.
ff Represents the two most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the hundredths of a second in a date and time value.
fff Represents the three most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the milliseconds in a date and time value.
ffff Represents the four most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the ten thousandths of a second in a date and time value. While it is possible to display the ten thousandths of a second component of a time value, that value may not be meaningful. The precision of date and time values depends on the resolution of the system clock. On Windows NT 3.5 and later, and Windows Vista operating systems, the clock’s resolution is approximately 10-15 milliseconds.
fffff Represents the five most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the hundred thousandths of a second in a date and time value. While it is possible to display the hundred thousandths of a second component of a time value, that value may not be meaningful. The precision of date and time values depends on the resolution of the system clock. On Windows NT 3.5 and later, and Windows Vista operating systems, the clock’s resolution is approximately 10-15 milliseconds.
ffffff Represents the six most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the millionths of a second in a date and time value. While it is possible to display the millionths of a second component of a time value, that value may not be meaningful. The precision of date and time values depends on the resolution of the system clock. On Windows NT 3.5 and later, and Windows Vista operating systems, the clock’s resolution is approximately 10-15 milliseconds.
fffffff Represents the seven most significant digits of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the ten millionths of a second in a date and time value. While it is possible to display the ten millionths of a second component of a time value, that value may not be meaningful. The precision of date and time values depends on the resolution of the system clock. On Windows NT 3.5 and later, and Windows Vista operating systems, the clock’s resolution is approximately 10-15 milliseconds.
F Represents the most significant digit of the seconds fraction; that is, it represents the tenths of a second in a date and time value. Nothing is displayed if the digit is zero.
: Represents the time separator defined in the current DateTimeFormatInfo..::.TimeSeparator property. This separator is used to differentiate hours, minutes, and seconds.
How to Enable Autologon for Windows Server 2008 Member Servers and Windows 7 Member Workstations
0Once you join a server to a domain, Windows will automatically delete the AutoAdminLogon value from the HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon registry key. This causes the userpasswords2 control to hide the “Users must enter a user name and password to use this computer” checkbox shown above.
Here’s how to get the missing checkbox back and configure Autologon:
- Open a CMD prompt and enter the following (all on one line):
reg add “HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon” /v AutoAdminLogon /t REG_SZ /d “1” /f
- Click Start, Run and enter control userpasswords2
- Clear the checkbox for Users must enter a user name and password to use this computer and click OK
- Enter the user name and password that will be used for Autologon and click OK
When the computer starts up the account you specified will be logged in automatically. Note that the password is encrypted on the computer.
This tip works for Windows 7, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2008 R2.